When you absolutely have to recruit patients on time
Home Our Locations Clinical Trials in the USA
Clinical Trials in the USA
For decades clinical trials in the USA have continuously been in high demand among pharmaceutical and biotechnological companies. The most prominent reasons for selecting the United States for clinical research are a large population pool, a developed network of experienced investigators, a supportive regulatory framework, and a vast market of drug consumption.
Accell’s team has decided to investigate what makes the USA such a favorable destination and the world’s principal hub for clinical research. So, we looked at the subject from different points of view varying from the USA’s geographical position, economic, and political status to its end-market advantages.
• USA health statistics & healthcare system overview
• Drug consumption market in the USA
• History of clinical trials in the USA
• USA regulatory landscape overview
• Current clinical trials situation in the USA
• Why partner with Accell for clinical research in the USA
⠀
Country’s overview
The United States of America is the third biggest country in the world, with the world’s most significant economic power measured in terms of gross domestic product (GDP). Politically, the USA is a federal republic with the federal government comprised of the three branches:
By 2019 estimates [1], almost 330 million people live in the U.S., which makes it the third most populated country after China and India. The main characteristics of the U.S. population is its great racial, national, and ethnic diversity due to a global immigration phenomenon. Interestingly, the nine most populous U.S. states (California, Texas, Florida, New York, Pennsylvania, Illinois, Ohio, Georgia, North Carolina) contain slightly more than half of the total population. The largest state in terms of its population is California, with 39.6 million residents.
⠀
USA Health Statistics & Healthcare System Overview
According to the National Center of Health Statistics, life expectancy in the USA has recently increased from 77.8 (2006) to 78.6 (2016) years. Women still live longer (80.3 to 81.1 years) than men do (75.2 to 76.1 years) [2]; nonetheless, the dominant causes of deaths remain the same for both sexes: heart disease, cancer, Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease, diabetes, stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, and unintentional injuries. Optimistically, for the past ten years (2006-2016), a steady decrease has been recorded in deaths from heart disease, stroke, cancer, and diabetes. However, the number of deaths from Alzheimer’s disease has significantly increased [3].
The U.S. is famous for being the country with the best medical help worldwide. The country is home to such well-known hospitals as Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, Johns Hopkins Hospital, and Massachusetts General Hospital. It is essential to keep in mind that most of the healthcare facilities in the USA are private, and their services are pricey.
Healthcare insurance system in the USA
Since healthcare comes at a high cost, in the United States, citizens must have proper healthcare insurance. They usually obtain their health insurance through employment; however, it is possible to purchase insurance privately or through government-based programs, e.g., Medicare, Medicaid, Veterans Administration, or other military care.
Alternatively, some low-cost or free of charge healthcare services exist through non-profit organizations, charities, and publicly funded programs. The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (known as Obamacare) was signed in 2010. It aimed at the expansion of insurance coverage. The program had many opponents, and it still is under debate with parties being on both ‘for’ and ‘against’ sides.
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) ranks the USA as the first country in the world by the spending of state funds for healthcare. In 2017, the expenditure was $10,206.5 per capita (or 17.1% of GDP). For comparison, Switzerland takes second place with 12.3% of GDP, and France comes third with 11.3% of GDP along with Germany with 11.2% of GDP. [4]
Despite prominent national spending on healthcare, the costs of medical services and lack of insurance coverage make Americans with lower incomes struggle to have adequate access to medical care. This situation is one of the reasons why these populations can get highly interested in participating in clinical trials and getting an opportunity to receive so much needed medical help.
⠀
Drug Consumption Market in the USA
The USA undoubtedly is the biggest pharmaceutical market in the world. By the second half of 2018, total pharmaceutical sales in the United States were estimated to reach about 464 billion U.S. dollars that year, which was 20 billion dollars more than the previous year [5]. Net medicine spending was $1,044 per person that is 0.9% (or $10) higher than in 2017. The primary factor that influenced the total net spending growth was the fact that patients were receiving existing branded drugs along with using newly launched ones.
- Currently, the most prominent players on the American pharmaceutical market are
- Pfizer Inc. with turnover of 25.32 billion USD;
- Johnson & Johnson (23.28 billion USD);
- Roche Holding AG (22.76 billion USD);
- AbbVie Inc. (USD 21.52 billion USD).[6]
Top-selling drugs are AbbVie’s Humira, Celgene’s Revlimid, Amgen’s Enbrel, and Roche’s Rituxan.
According to the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers Association (PhRMA), U.S. firms conduct over half the world’s research and development (R&D) in pharmaceuticals (75 billion dollars) and hold the intellectual property rights on the newest medicines. [7] The total number of biotech and pharmaceutical companies in the USA surpasses 2,700 [8].
⠀
History of Clinical Trials in the USA
Certain medical historians name the USA a cradle for the scientific approach to investigation of safety and efficacy of marketed drugs (as stated by Harry Marks, the author of “The Progress of Experiment: Science and Therapeutic Reform in the United States, 1900-1990”).
In 1905 American Medical Association (AMA), the largest association of physicians and medical students in the United States, founded in 1847, formed its own Council on Pharmacy and Chemistry with the primary goal to reveal safe and efficient drugs among placebos with big names. Since then, only medications approved by the Council could hold AMA’s seal and be advertised in AMA’s journal. To receive approval, manufacturers had to run a preclinical trial to prove an ingredient’s purity. After that, the Council on Pharmacy and Chemistry followed rudimentary efficacy and safety tests. In 1906 the Pure Food and Drugs Act proclaimed the Bureau of Chemistry as the official market regulator responsible for taking of adulterated and misbranded products.
In the 1920s, first multicenter trials were implemented in the USA to reduce possible mistakes of individual observers.
Later, in 1938, the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act came in force. The Federal Act gave authority to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to oversee the safety of food, drugs, medical devices, and cosmetics. The FDA itself is a federal agency founded in 1906 and responsible for protecting and promoting public health up to this day.
The 1938’s Act obliged drug manufacturers to submit safety data to FDA officials for evaluation before marketing. Soon New Drug Application rules were elaborated that required stating information about all performed preclinical and clinical research. Hence, a standardization process of preclinical and clinical tests of new drugs along with standards for clinical trial conduct started.
In the 1960’s, the Drug Amendments and investigational drug regulations obliged drug developers to run studies on animals before testing a drug on humans. Besides, controlled trials to prove the drug efficacy became necessary.
Since then, the FDA has developed a full package of standards and recommendations in the field of clinical trials and drug development. Recent FDA’s efforts concentrate on speeding up of more effective drugs appearance on the market and lowering of clinical trials costs. For instance, currently, the FDA works on the implementation of surrogate parameters in oncology studies and risk-based monitoring.
⠀
USA Regulatory Landscape Overview
In the USA, all food, drugs, cosmetics, and medical devices for both humans and animals, are regulated under the authority of the United States Food and Drug Administration, widely known as the FDA. Only after a review of the FDA and Institutional Review Boards (IRBs), clinical trials in humans can start. [9]
To initiate a clinical trial, a sponsor should submit to the FDA an Investigational New Drug (IND) Application with the content specified in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) 21, section 312, and should wait 30 days before the trial initiation. During this time, the FDA has an opportunity to review the documents and authorize the trial. Usually, a new drug application can be submitted when the drug successfully passes all three phases of clinical trials.
Given the fact that the USA’s pharmaceutical market is a desirable destination for many companies, it is worth noticing that clinical research does not have to be exclusively held within the United States to receive an FDA’s authorization. This particular notion can be beneficial to those companies, especially small or emerging ones with limited trial budgets, who want to optimize their expenditures and enter the end-market with their product faster.
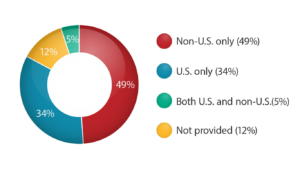
According to the clinicaltrials.gov information [10], 58% of recruiting studies are “Non-U.S. only.” This number demonstrates clearly that almost 2/3 of all FDA-registered studies take place outside the United States.
Thus, to enter the USA market, you can hold a trial in other geographies. FDA registers the study results given the fact that everything was compliant with ICH-GCP and FDA’s regulations. Moreover, the FDA continually monitors the quality of clinical trials both in the USA and outside the country: the agency regularly conducts audits in various countries and publishes the findings. [11]
⠀
Current Clinical Trials Situation in the Country. Is it worth running clinical research in the USA?
In 2018 the United States was the top location for global clinical trials taking up 35% of the total number of geographies. Countries following the USA in the clinical research global arena were China (10%), Japan (5.2%), India (3.8%), and Germany (3.8%) rounding out the selection of the top five countries. According to the data on www.clinicaltrials.gov, by mid-2019, there are over 322,000 research studies registered worldwide where over 100,000 studies take place within the USA. These numbers mean that over 30% of all registered globally studies are held exclusively in the United States; however, the data shows that 49% of global studies happen strictly outside of the USA. [12]
⠀
Percentage of Registered Studies by Location
(in accordance with www.clinicaltrials.gov as of December 11, 2019)
Typically, only late phase (II and III) clinical trials require global coverage to make sure that they involve larger populations and a high number of both sites and patients. So, it makes perfect sense for many companies to run an early phase clinical research locally and preferably in the USA since most pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms are based in the region.
To facilitate and speed up recruitment, the most populated territories in the USA are of interest to pharmaceutical companies, biotechs, and clinical research organizations (CROs). The most clinical trial concentration is within such states as California, New York, and Texas, while Wyoming, Alaska, North Dakota, Hawaii, Maine, and Vermont remain mostly excluded from the competition with just a few studies listed. [13]
⠀
Number of Registered Clinical Trials in the USA
(in accordance with www.clinicaltrials.gov as of December 11, 2019)
According to Accell’s internal data analytics system, in the second quarter of 2019, the majority of trials initiated in the United States was in oncology and central nervous system (CNS). With a noticeable gap, trials in infectious and cardiovascular diseases share the third place.
What makes the USA an attraction for sponsors is its robust regulatory system, developed investigators network, large population, the English language, and a vast potential of market’s drug consumption.
Pitfalls of running a clinical trial in the USA
Despite all benefits that running a clinical trial in the USA brings to a Sponsor, it is essential to know about certain complexities and risks involved in the process. First and foremost, the risk factor is patient recruitment and retention. The numbers are brutal: 48% percent of sites miss their enrollment targets [14], and 80% of trials are delayed due to recruitment [15].
The USA’s clinical research market is oversaturated, with various trials running simultaneously. Thus, there is a continually increasing competition for patients. It is a basic mathematics to count that the USA has one clinical trial for every 2,582 people. We can compare the data with Eastern Europe, where there is one clinical trial for every 6,975 or post-Soviet countries with a clinical trial ratio of one to 89,884 people. These numbers demonstrate that a “fight” for each patient is a severe endeavor in the States, especially given the fact that in the USA’s most medical practices are private with no central database of specific patients. So, each patient is searched for and enrolled on a case by case basis. Moreover, the recruitment is hugely dependent on the proactive work of an investigator. Yet, data shows that 27% of U.S. investigators fail to enroll any subjects in comparison with 19% of investigators elsewhere [16].
Another factor influencing recruitment and, precisely, retention rate, is the domestic migration rate within the USA. Citizens face no cultural or nationally regulated barriers for moving from one state to another. Hence, there is a probability that a patient can easily drop out of a study if they move to a different location.
Finally, per-patient cost for clinical trials in the USA is high in comparison to other regions. Although in a certain way, logistics can be cheaper within the States than shipping drugs and bio-samples overseas, investigators’, sites’, and CROs’ services come at a substantial cost to a Sponsor. As an example, taking “1” as a total cost of a clinical trial in the USA, a Sponsor will have 0.5 in Germany, Brazil, or China, 0.41 in Russia, 0.39 in Poland, and 0.36 in India [17].
To sum up, we could assume that the USA is generally a good location for a smaller Phase I trial with healthy volunteers or a limited number of needed for recruitment patients. However, for a more extensive Phase II and III trials, it would be a wise strategy to look for various clinical trial geographies options. In the meantime, it can be reasonable not to eliminate the USA, especially if a Sponsor wants to enter the U.S. market with their drug but reduce it just to a certain statistically required number of patients while concentrating the efforts on recruitment in other regions. At Accell, we highly recommend studying more closely such potent geographies for clinical research as Eastern Europe and post-Soviet states (if Caucasian population is statistically needed), India (primarily Indo-Aryan population), and China (Asian population).
⠀
Why selecting Accell as a research partner within and outside the USA?
Accell Clinical Research, LLC is an American based company founded in 2007 that delivers high-quality, full-service clinical research services for over a decade. While concentrating mostly on the Eastern European region for its numerous benefits, we have been conducting multicenter clinical trials with U.S. sites as well. Most of our Sponsors are small and medium-size American pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies with headquarters and primary R&D activities in the USA.
Depending on the stage of a trial and a required number of patients for recruitment, Accell suggests an optimal international strategy for a particular study to make sure a Sponsor gets involved with only well-performing and trusted investigators who work at high recruiting sites. Accell’s ultimate goal is to recruit patients on time and within a budget making each research project a cost-effective one.
Throughout the past decade, Accell participated in 11 global clinical trials with sites both within and outside the USA with American and European sponsors. Our vast experience in regulatory processes and comprehensive cooperation with U.S. partners renders us the right company to work with on the USA’s territory. Accell’s advantageous geographical positioning with offices and staff located in the USA, Europe, Russia, and Ukraine facilitates to share responsibilities between regions. It makes our model optimal, efficient, and cost-effective.
⠀
The article is written by Kirill Zhuravlev, MD, PhD (Medical Director) and Olga Nayanova (Business Development Associate). The article was updated on November 27, 2019.
⠀
References:
- Internet World Stats
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2) – Health, United States, 2017
- OECD.Stat – Health, Health Expenditures, and Financing
- Statista (1)
- Market Research Reports
- SelectUSA
- Statista (2) – U.S. number biotech companies 2012-2016
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- ClinicalTrials.gov – Locations of Recruiting Studies
- FDA – Clincial Investigator Inspection Search
- ClinicalTrials.gov – Types of Registered Studies
- ClinicalTrials.gov – Studies in the United States
- Tufts CSDD Impact Report, 2013, 15(1)
- Drugdevelopment-technology.com, 2012, Clinical Trial Delays: America’s Patient Recruitment Dilemma
- NCBI – The State of Clinical Research in the United States: An Overview
- NCBI – Challenges in Clinical Research
Our Locations
The top ten largest American cities with a population of over a million inhabitants are:
⠀
- New York City, NY – 8.6 million
- Los Angeles, CA – 4 million
- Chicago, IL – 2.6 million
- Houston, TX – 2.3 million
- Phoenix, AZ – 1.7 million
- Philadelphia, PA – 1.5 million
- San Antonio, TX – 1.5 million
- San Diego, CA – 1.4 million
- Dallas, TX – 1.3 million
- San Jose, CA – 1 million
discover Accell’s geography country by country

Belarus
Non-EU
60 days for regulatory approval
9.5 million population

Bulgaria
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
7.1 million population

Croatia
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
4.1 million population

Estonia
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
1.3 million population

Georgia
Non-EU
28-56 days for regulatory approval
3.7 million population

Hungary
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
9.8 million population

Kazakhstan
Non-EU
10 business days for regulatory approval | 17.8 million population

Latvia
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
1.96 million population

Lithuania
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
2.8 million population

Montenegro
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
622 781 population

Poland
EU
75 days for regulatory approval
37.95 million population

Romania
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
19.71 million population

Russia
Non-EU
60 days for regulatory approval
144.3 million population

Serbia
EU
60 days for regulatory approval
7 million population

Ukraine
Non-EU
60 days for regulatory approval
45 million population

Israel
Non-EU
60-90 days for regulatory approval
8.7 million population
USA
North America
30-90 days for regulatory approval
327.2 million population
This Is Your Team. We Make Clinical Trials Happen.